Removal of Carbon Dioxide from Natural Gas by Vacuum Pressure Swing Adsorption
Removal of Carbon Dioxide from Natural Gas by Vacuum Pressure Swing Adsorption
abbas bakhtom
Removal of Carbon Dioxide from Natural Gas by Vacuum Pressure Swing Adsorption
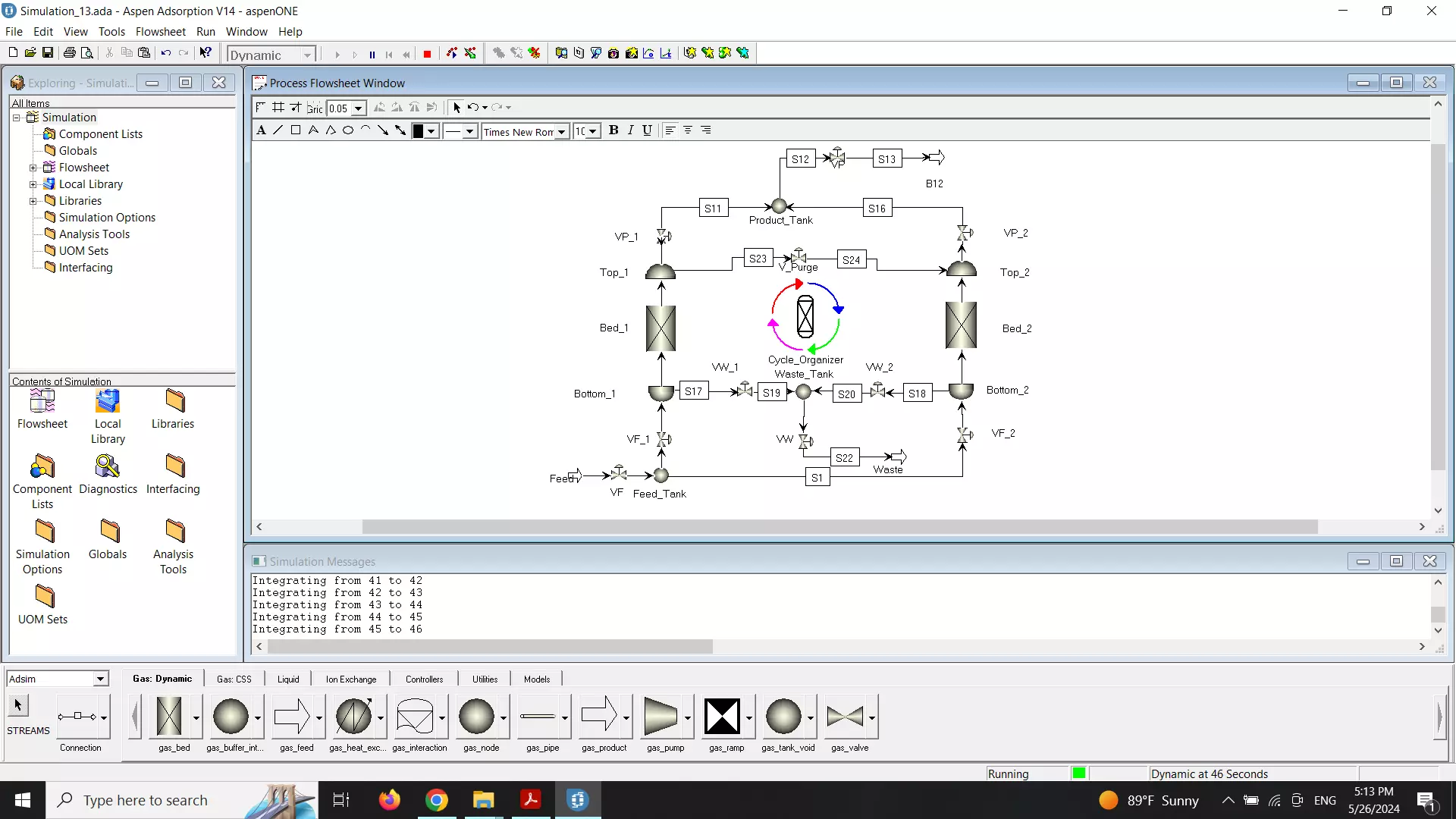
A vacuum pressure swing adsorption (VSA-PSA) process is studied for the removal of carbon dioxide in a contaminated stream of natural gas to achieve fuel grade methane. The adsorbent used was zeolite 13X (CECA) where CO2 is strongly adsorbed. A Skarstrom-type cycle comprising pressurization with product, feed, countercurrent blowdown, and countercurrent purge was employed. A mixture having 60% CH4/20% CO2/ 20% N2 was used, and two different temperatures were evaluated in a single-column VSA-PSA unit. Under the conditions tested, CO2 was removed to levels lower than 2% as required by fuel grade methane with methane recovery higher than 80% without recycle. This separation process also helps in the CH4-N2 separation. A bidisperse (macropore-micropore) model also including distributed energy balances in gas, solid, and column wall considering heat and mass transfer resistance at the gas-solid interface was used to simulate the VSAPSA behavior and compare with experiments.
6 خرداد 1403
مهارتهای استفاده شده
6 خرداد 1403